Armenia Lost Nagorno-Karabakh After Three Decades of Conflict with Azerbaijan
3 min read
For over thirty years, the Nagorno-Karabakh region has been at the heart of a bitter dispute between Armenia and Azerbaijan, resulting in a tragic loss of life and countless displaced individuals. Millions have suffered, forced into homelessness by the ongoing turmoil, and more recently, over 50,000 people have been compelled to abandon their homes.
The Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh has spanned three decades, making it one of the most enduring disputes in recent history. This Armenian-Azerbaijani dispute, rooted in the complex Nagorno-Karabakh history, reached a pivotal moment with Armenia’s defeat in Nagorno-Karabakh. Azerbaijan emerged as the victor in this protracted conflict, leading to a Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire agreement.
The international impact of Nagorno-Karabakh has been significant, drawing the attention of global powers and organizations. Recent developments in Nagorno-Karabakh continue to shape the region’s dynamics, with lasting implications for the parties involved and the broader geopolitical landscape.
The Roots of the Conflict
Nestled between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, the South Caucasus region hosts Armenia and Azerbaijan, neighboring countries akin to India and Pakistan. It is within this region that Nagorno-Karabakh, a territory claimed by both nations, lies at the core of a long-standing conflict. Armenia and Azerbaijan, once part of the Russian, Ottoman, and Persian Empires, emerged as independent nations in 1918 following the collapse of the Russian Empire.
The religious divide between Christian-majority Armenia and Muslim-majority Azerbaijan created fertile ground for conflict. The Soviet Union’s intervention in the form of border delineation and the allocation of Nagorno-Karabakh to Azerbaijan only fueled tensions. The region, marked by its mountainous terrain, became emblematic of national identity for both countries.
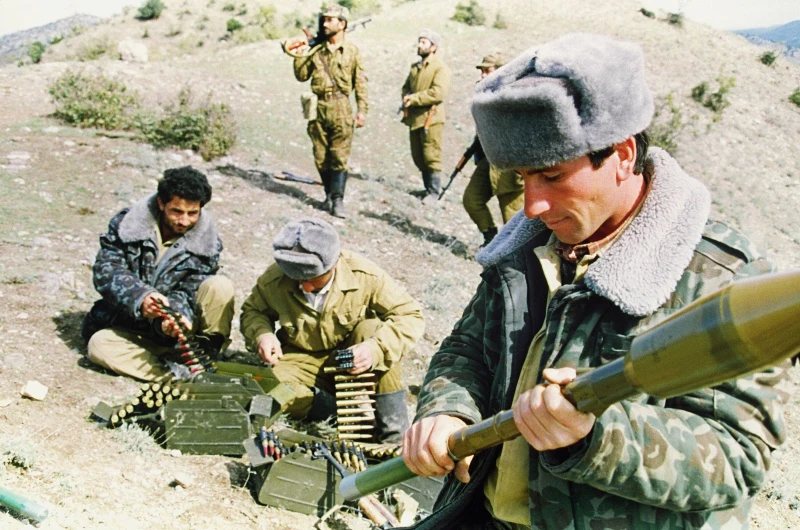

The Road to War
While the conflict simmered for years, it did not erupt into full-scale war until 1985, driven by the weakening Soviet Union. In 1988, the Nagorno-Karabakh Assembly’s resolution, rejecting autonomous status and favoring union with Armenia, exacerbated the situation, leading to the eventual declaration of independence by both Armenia and Azerbaijan in 1991. Two years of intense warfare ensued, claiming over 30,000 lives. Armenia’s occupation of substantial Nagorno-Karabakh territory marked a turning point.
Ceasefires and Renewed Conflict
In 1994, Russia brokered a ceasefire, formalizing the status quo – the occupying force retaining control. The Armenia-Azerbaijani conflict, though seemingly quelled, remained volatile. In 2020, a 44-day war erupted, with Azerbaijan reclaiming lost territories. Russian intervention secured another ceasefire, leaving Armenia with a reduced foothold in the region. However, the peace was short-lived. In 2022, clashes reignited, culminating in Azerbaijan’s recent invasion.
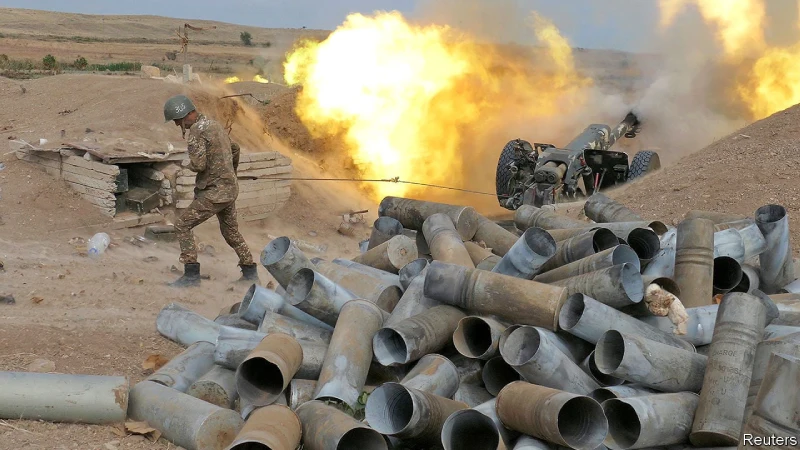

The Global Players
Behind this enduring conflict stand significant global players, with Russia and Turkey at the forefront. Russia has consistently supported Armenia, while Turkey has staunchly backed Azerbaijan, emphasizing the need to address Turkey’s relevance to India. Moreover, Turkey’s historical and cultural ties with Azerbaijan, bolstered by energy pipelines passing through the conflict zone, have cemented its support. Turkey’s military assistance, including F-16 fighter jets and drones, proved instrumental in Azerbaijan’s 2020 victory.
India’s Dilemma
India, with favorable relations with both Armenia and Azerbaijan, leans slightly towards Armenia, largely due to Armenia’s stance on the Kashmir issue. India has even supplied arms to Armenia, sealing a $250 million arms deal in 2022. As the conflict persists and Turkey and Pakistan align with Azerbaijan, India’s role in balancing these delicate diplomatic ties remains paramount. The ongoing turmoil, including the dispute over a land corridor, suggests that the Nagorno-Karabakh issue continues to impact international dynamics.
#NagornoKarabakh #Geopolitics #India #Armenia #Azerbaijan #Turkey