NASA congratulates ISRO on the successful Chandrayaan-2 launch
6 min read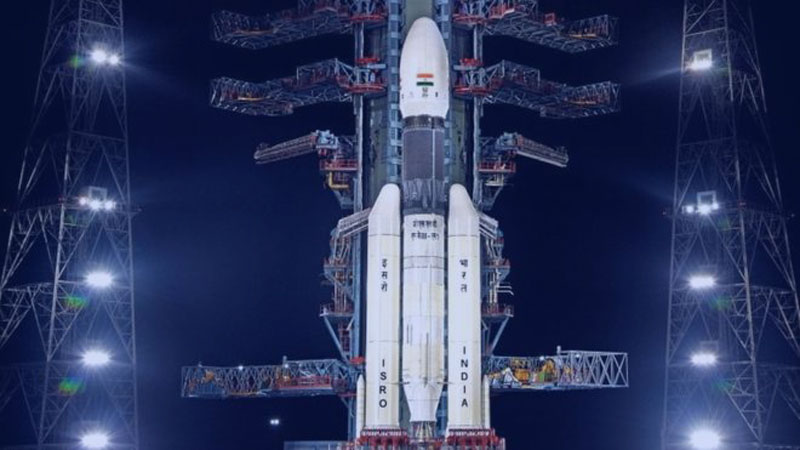
Chandrayaan-2 was a lunar exploration mission launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 2019. The mission aimed to land a rover on the moon’s surface and carry out scientific studies of the lunar surface, including mapping the moon’s surface, searching for water and minerals, and studying the moon’s atmosphere.
The mission was launched on July 22, 2019, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India, using the GSLV Mk III rocket. The spacecraft successfully entered lunar orbit on August 20, 2019, and the rover, called Pragyan, was scheduled to land on the moon’s surface on September 6, 2019. However, the rover was not able to make a successful landing and the mission ended in failure.
Despite the failure of the landing, the mission was still considered a success because the spacecraft was able to complete a number of other important objectives, including mapping the moon’s surface, studying the moon’s surface composition, and studying the moon’s exosphere. The mission also made a number of important scientific discoveries, including the detection of water molecules on the moon’s surface, and helped to advance our understanding of the moon and its environment.
Table of Contents
NASA congratulated ISRO for Chandrayaan-2 Mission Success

NASA on Monday respect its Indian companion, ISRO on the solid dispatch of its second moon mission Chandrayaan-2, and accepted it was seeing forward to comprehending what the Indian space organization gets about the lunar south post.
India on Monday launched a spacecraft using the most powerful rocket, the Launching Vehicle of the Geosynchronous Mark III (GSLV Mk-III) Satellite from the Satish Dhawan space center in Sriharikota Andhra Pradesh.
India made a big leap in the space program on Monday after the space agency launched a spacecraft scheduled to land on the Moon in September.
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), which is equivalent to India for NASA, confirmed the successful launch of the spacecraft when the country drew closer to becoming only the fourth country – after the United States, China, and Russia – to land spacecraft on the Moon. Chandrayaan-2 aims to land on a plain surface that covers the ground between the two Moon craters, Simpelius N and Manzinus C.
Relevance of Chandrayaan-2 mission:

The Chandrayaan-2 mission, which was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in July 2019, was a significant milestone in the country’s space exploration program. The mission’s primary objective was to land a rover on the lunar surface and explore the moon’s south polar region, which is believed to contain water ice.
The mission was also designed to study the moon’s surface and its mineral and chemical composition, as well as measure its surface temperature and search for signs of water ice. It carried a suite of scientific instruments, including a camera, a spectrometer, and a radar, to gather data about the moon’s surface and subsurface.
In addition to its scientific objectives, the Chandrayaan-2 mission was also seen as a major technological achievement for India, as it marked the country’s first attempt at a soft landing on the moon. The mission’s rover, named Vikram, was able to successfully land on the lunar surface, but unfortunately lost contact with the ground station shortly thereafter. Despite this setback, the mission was still considered a success overall due to the data and other scientific observations it was able to collect.
Overall, the Chandrayaan-2 mission was a significant achievement for India and contributed to our understanding of the moon and its potential resources. It also demonstrated India’s capabilities in space exploration and demonstrated the country’s commitment to advancing its space program.
Importance of Chandrayaan-2 launch:
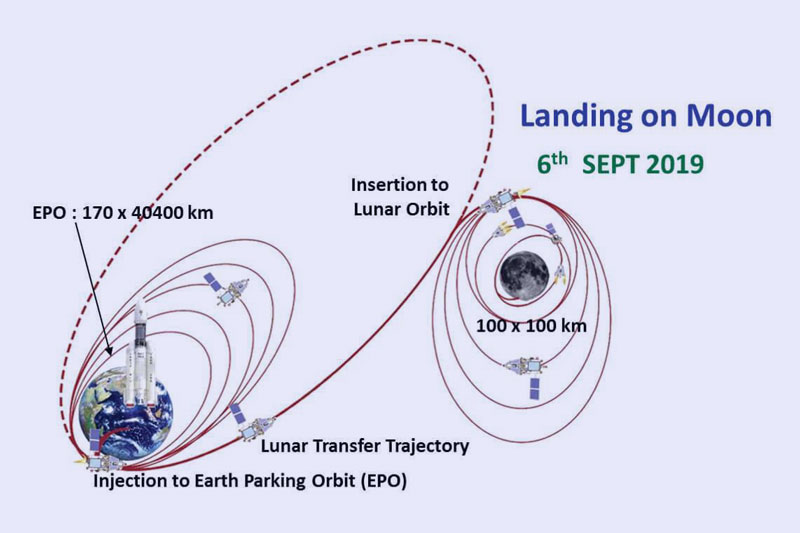
Organization (ISRO) in July 2019, was a major milestone in India’s space exploration program. It marked the country’s first attempt at a soft landing on the moon and was designed to study the moon’s surface and its mineral and chemical composition, as well as measure its surface temperature and search for signs of water ice.
The mission was considered a major technological achievement for India and demonstrated the country’s capabilities in space exploration. It also showed India’s commitment to advancing its space program and contributing to our understanding of the moon and its potential resources.
In addition to its scientific and technological significance, the Chandrayaan-2 mission also had a number of practical implications. For example, the data and observations collected by the mission’s rover and other instruments could help to identify potential lunar resources that could be exploited for future space exploration and colonization efforts. The mission could also help to pave the way for future manned missions to the moon and other celestial bodies.
Overall, the Chandrayaan-2 mission was an important step forward for India’s space program and contributed significantly to our understanding of the moon and its potential for exploration and development.
What do we learn from the successful launch of Chandrayaan-2?

Chandrayaan-2 was an Indian lunar mission that was successfully launched on July 22, 2019, and consisted of an orbiter, a lander called Vikram, and a rover called Pragyan. The mission’s primary goal was to land on the south pole of the Moon and conduct scientific experiments to study the lunar surface and search for water and other resources.
The successful launch and subsequent landing of Chandrayaan-2 demonstrated the capabilities of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in conducting complex space missions and advanced technologies such as autonomous navigation and landing systems. It also highlighted the potential for international cooperation, as the mission included contributions and technology from various countries and organizations.
Chandrayaan-2 also conducted several scientific experiments during its mission, including mapping the surface of the Moon and studying its composition and mineralogy. The mission’s results have provided valuable insights into the history and evolution of the Moon, and have helped to further our understanding of the solar system and the universe as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
Chandrayaan-2 is an Indian lunar mission that was launched in July 2019 with the goal of landing a rover on the Moon’s south polar region.
The main objectives of Chandrayaan-2 were to demonstrate India’s capabilities in inter-planetary exploration, study the surface of the Moon and its mineral and chemical composition, and search for water ice in the south polar region.
Chandrayaan-2 successfully entered lunar orbit, but the rover lander (Vikram) was unable to land on the surface of the Moon due to a technical issue. However, the mission was still considered a success as it achieved many of its other objectives, including sending back high-resolution images of the lunar surface and conducting a number of scientific experiments.
Chandrayaan-2 was a collaboration between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and a number of other organizations, including the Lunar Exploration and Remote Sensing Satellite (LERSS), the Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN), and the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA).
Chandrayaan-2 was the second lunar mission undertaken by India, following the successful Chandrayaan-1 mission in 2008. It was also the first mission to land a rover on the south polar region of the Moon. Overall, Chandrayaan-2 was a major achievement for India’s space program and a significant milestone in lunar exploration.






